電腦視覺與虛擬實境組
COMPUTER VISION & VR GROUP
TARGETS
Vision Group

INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM

ASSISTIVE ALARMING SYSTEM

PEDESTRIAN & VEHICLE DETECTION
VR Group

ACTION RECOGNITION

HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION

AUGMENTED REALITY
RESEARCH
基於多任務之人臉資訊偵測深度學習模型
A Deep Multi-task Model for Face Information Detection
本論文提出了第一個以全臉影像作為輸入同時進行頭部姿態估計、眼睛狀態偵測和視線狀態估計的深度學習模型。我們使用多任務學習的方式,以單一模型進行推論,進而避免使用多個模型進行預測時需要大量記憶體的情況。為了能讓棋型在每個任務分支中能夠分辨出自身需要的特徵,我們設計跨維度注意力模組來為每個分支增強並篩選出對於各自任務所需要的特徵。此外,為了解決開閉眼狀態資料集沒有包含多角度頭部姿態的問題,我們提出生成具有眼睛狀態標註資料的資料擴增技術,提升模型在不同角度頭部姿態開閉眼偵測的穩定性。
In this paper, we present a lightweight multi-task deep learning model that utilizes full-face images to detect head pose, gaze direction, and eye state simultaneously. We propose a task-based cross-dimensional attention module that selectively filters and enhances relevant features for each specific task. Additionally, to tackle the lack of diverse head pose angles in the eye state dataset, we introduce a data augmentation technique to generate eye state data under different head poses, enhancing the model's robustness in detecting eye states under varying head poses.
基於深度學習之強健性即時道路標記偵測系統
Deep Learning-based Robust Real-time Road Marking Detection System


本論文提出了一種包含兩個階段的深度學習系統來解決現有偵測架構中難以辨識高度扭曲的路面標記以及難以平衡召回率以及準確率的路面標記偵測架構,本系統可在各種環境下即時準確的偵測地面標記。本論文還建立了一個新的路面標記偵測與分類的基準,收集的資料庫包含11800張高解析度影像。這些影像是在不同的時間和天氣狀況下拍攝於臺北的道路,並且手工標記出13種列別的候選框。實驗證明本論文提出的架構在路面標記偵測的任務中超過其他物件偵測架構。
In recent years, Autonomous Driving Systems (ADS) become more and more popular and reliable. Road markings are important for drivers and advanced driver assistance systems better understanding the road environment. While the detection of road markings may suffer a lot from various illumination, weather conditions and angles of view, most traditional road marking detection methods use fixed threshold to detect road markings, which is not robust enough to handle various situations in the real world. To deal with this problem, some deep learning-based real-time detection frameworks such as Single Shot Detector (SSD) and You Only Look Once (YOLO) are suitable for this task. However, these deep learning-based methods are data-driven while there are no public road marking datasets. Besides, these detection frameworks usually struggle with distorted road markings and balancing between the precision and recall. We propose a two-stage YOLOv2-based network to tackle distorted road marking detection as well as to balance precision and recall. Our network is able to run at 58 FPS in a single GTX 1070 under diverse circumstances. In addition, we propose a dataset for the public use of road marking detection tasks. The dataset consists of 11800 high resolution images captured at distinct time under different weather conditions. The images are manually labeled into 13 classes with bounding boxes and corresponding classes. We empirically demonstrate both mAP and detection speed of our system over several baseline models.
多感測器前端融合之深度學習應用於自駕車
A research on early fusion based on multi-sensor

將多感測器間的資訊透過透過深度學習各自進行特徵擷取,各感測器擷取的特徵投影製相同的座標系,將這些特徵在特定通道上串接在一起得到融合後的特徵 ,進行前端的融合後,各感測器間可以利用彼此的優點截長補短,以得到良好的特徵。我們發展出一連串以電腦視覺(computer vision)為基礎的技術,其技術應用於障礙物偵測(行人或車輛偵測)。
The information between multiple sensors is collected through deep learning for individual feature collection. The features collected by each sensor are projected to the same standard system, and these features are connected to a specific channel to obtain the fused feature. After the early fusion, each sensor can take advantage of each other to cut short complements to obtain good features. We have developed a series of techniques based on computer vision techniques are applied on obstacle detection (such as pedestrian or vehicle detection).
個人化的動作辨識
User-Specific Motion Recognition

個人化動作辨識研究之目的在於想要建立一個可靠的通用型動作辨識系統,其中之困難處在於適應不同使用者有不同的動作習慣與外觀,針對這些難題尋求解決之道,則將可以迅速有效地建立個人化的動作辨識系統,進而運用在即時的互動應用,能以動作為輸入訊號融合於仰賴固定型態動作辨識的系統,提升未來日常生活上的便利性以及在虛擬實境的延伸技術上有多方面的發展。
This research focuses on developing a reliable and general action-recognition (AR) system, which is difficult to adapt various appearance and action styles of different users. Many future applications rely on this technique such as the real-time Human-Machine Interaction (HCI) systems due to the significance of identifying the input signal of a certain motion pattern, and are potentially used in extension techniques of AR as well as enhance the convenience of life.
虛擬實境
Virtual Reality
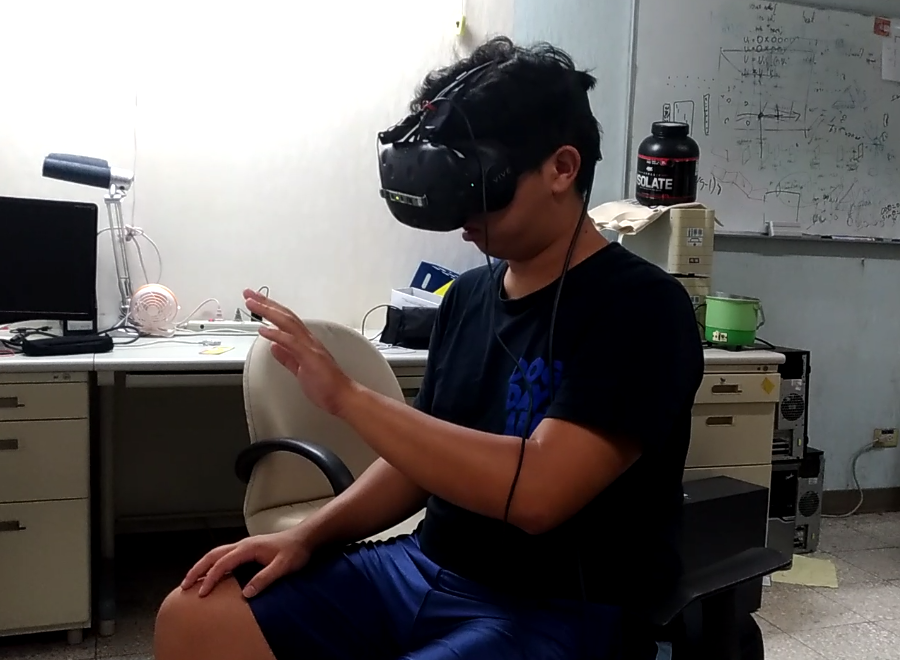

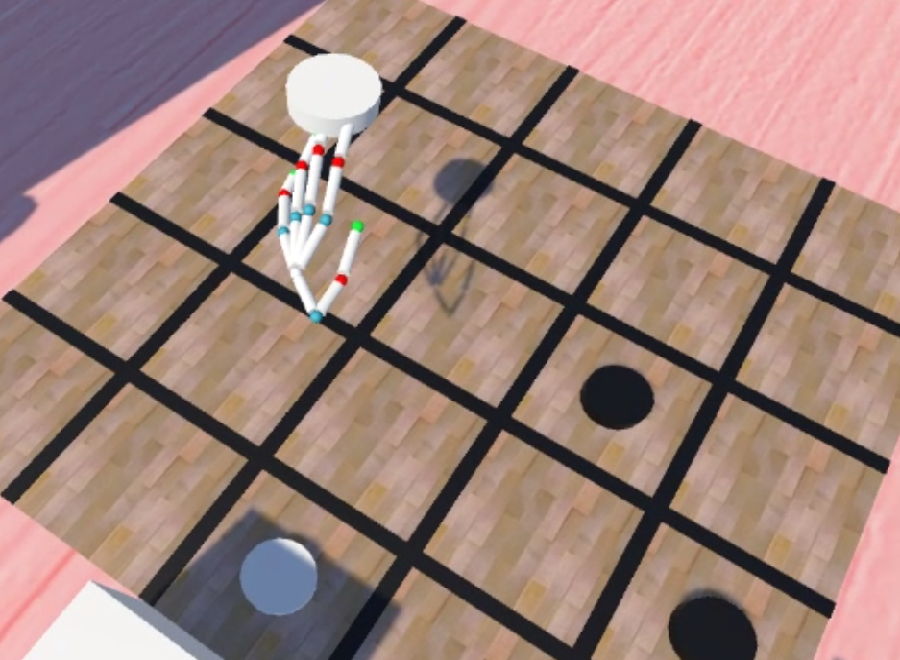
目前致力於手勢辨識與人機互動的應用,主要想要提供的是與電腦以及虛擬環境自然互動的方法。其中的困難之處在於手部多樣性的動作,手指與手指之間互相的遮蔽以及深度攝影機取得之影像中的缺失。在整個應用的流程中,首先以架設在頭盔上的深度攝影機取得影像,並以深度學習計算出手的關節在空間中的座標,並投影在虛擬環境中,並以此作為與虛擬物品互動的根據。
This research is now focusing on hand pose estimation and human-computer interaction, and we would like to propose a method to provide a natural way to interaction with the computer and the virtual environment. The difficulty of this includes hand pose variations, self-occlusion and depth image broken. The process of our application is listed below: we will first get the depth image from the depth camera which is set on the helmet, then estimation the 3D coordinates of the hand joint by deep learning. Finally, project the joint coordinates in to the virtual environment and interact with the object.
適合自動駕駛車輛之結合邊緣資訊即時影像語意分割系統
Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Edge Information for Autonomous Vehicle
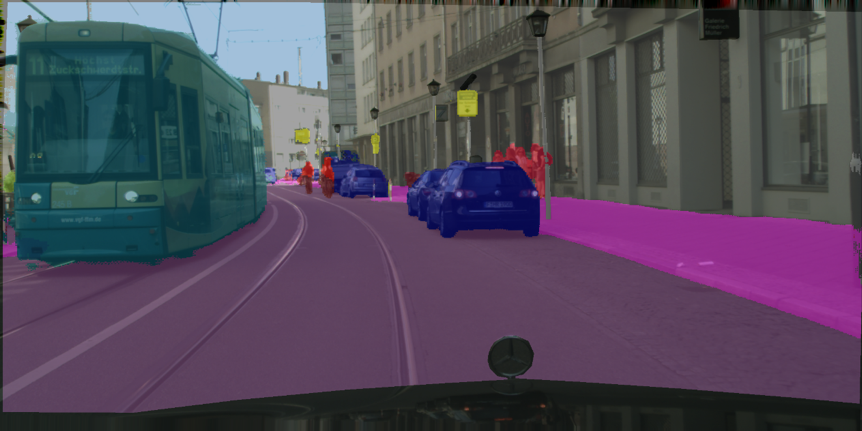

在先進駕駛輔助系統 (ADAS)中,其中一項基本功能需求是藉由影像切割功能找到車輛可以行駛的區域。有別於傳統影像切割方法,採用語意分割的深度學習網路架構,可以更正確辨識不規則的道路區域,指引自駕車行駛在更複雜的道路環境中。本研究中,首先分析最先進的即時影像語意分割系統的輸出。 由這些輸出結果顯示,大多數被錯誤分類的像素,都是位於兩個相鄰物件的邊界上。基於此觀察,本研究提出一種新穎的即時影像語意分割網路系統,它包含一個類感知邊緣損失函數模塊與一個通道關注機制,旨在提高系統準確性而不損害運行速度。
In Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), image segmentation for recognizing drivable areas and guiding the vehicle forward is a basic function. For the latter, unlike those traditional image segmentation methods, image semantic segmentation based on deep learning architecture can handle the irregularly shaped road areas better, guiding a vehicle to drive in a more complex environment. In our research work, we first analyze the output of state-of-the-art real-time semantic segmentation networks. The result shows that most of the misclassified pixels are located on the edge between two classes. Based on this observation, we propose a novel semantic segmentation network which contains a class-aware edge loss module and a channel-wise attention mechanism, aiming to improve the accuracy with no harm to inference speed.
MAC-RAD:透過從RGB視訊分離可重複使用資產模組實現模組化虛擬分身合成
MAC-RAD: Modular Avatar Composition via Reusable Assets Disentanglement from RGB Video
在本論文中,我們提出了一個兩階段模組化框架,用於從單目 RGB 影片中重建虛擬分身,旨在支援服裝級控制和虛擬分身組合。為此,我們定義了兩個階段,即解纏階段和組合階段。在解纏階段,我們的系統將輸入影片分解為具有語義意義的組件,包括皮膚紋理和一組帶有紋理的服裝網格,每個組件都與一個規範姿勢對齊,並由用戶提供的文字提示引導。此階段利用參數模型(例如 SMPL-X)進行姿勢和形狀估計,確保跨幀的一致性。
在組合階段,解纏後的組件將根據用戶的設定(例如體型和服裝選擇)重新組合成一個統一的、可動畫化的網格。產生的虛擬分身支援運動重新導向和渲染,同時支援靈活的服裝重組。
我們的框架強調模組化、可重複使用性和速度,允許快速創造虛擬分身,且僅需少量品質權衡。實驗結果展現了高度的視覺連貫性、服裝完整性以及對構圖的支援。作為未來的發展方向,我們設想在系統中擴展一個 CLIP 引導的服裝檢索模組。這將使用戶能夠通過自然語言描述進行直覺的、基於文字的虛擬分身編輯。
In this thesis, we present a two-stage modular framework for avatar reconstruction from monocular RGB videos, designed to support garment-level control and avatar composition. To this end, two stages are defined, namely, Disentanglement Stage and Composition Stage. In the Disentanglement Stage, our system decomposes input video into semantically meaningful components, including a skin texture and a set of textured clothing meshes, each aligned to a canonical pose and guided by user-provided textual prompts. This stage leverages parametric models (e.g., SMPL-X) for pose and shape estimation, ensuring consistency across frames.
In the Composition Stage, the disentangled components are reassembled into a unified, animatable mesh based on user-defined settings, such as body shape and clothing selection. The resulting avatar supports motion retargeting and rendering while enabling flexible garment recombination.
Our framework emphasizes modularity, reusability, and speed, allowing rapid avatar creation with only minor quality trade-offs. Experimental results demonstrate high visual coherence, garment integrity, and support for composition. As a future direction, we envision extending the system with a CLIP-guided garment retrieval module. This would enable intuitive, text-based avatar editing through natural language descriptions.
Keywords: Virtual Avatar, 3D Human Reconstruction, Modular Avatar Composition, Garment Disentanglement, Gaussian Splatting, Diffusion Model
AR遠端會議中的即時摘要與重播助理
ARM-RSPA: Augmented Reality Meeting with Real-Time Summarization and Playback Assistant
自疫情以後,遠端會議成為部分工作的常態,現在主流的會議系統如 Google Meet 與 Microsoft Teams 被廣泛使用。而隨著 AR/VR 技術的進步,虛擬會議能夠得到進一步的提升,並提供高度沉浸感與互動性的體驗給使用者。
傳統會議中,通常會有人整理會議並記錄以方便事後釐清內容;而現在視訊會議也有逐字稿等工具將講者的話轉錄下來,但在現在 VR/AR 的會議內,缺少記錄並輔助使用者的工具。因此我們提出了 ARM-RSPA,一個即時紀錄會議內容與虛擬環境狀態,並根據使用者要求摘要且重播關鍵的互動的助手系統。透過 AR 重播,ARM-RSPA 提供使用者更加方便且易於理解的方法。
在後面的實驗中,ARM-RSPA 展現出在會議中的運用,並成功幫助使用者理解講者所講解的內容。我們也探討 ARM-RSPA 與其他遠端會議的差別以及未來 AR 會議工具可能的發展。
Since the pandemic, remote meetings have become the norm for some work environments, with mainstream meeting systems like Google Meet and Microsoft Teams being widely used. With advancements in AR/VR technology, virtual meetings can be further enhanced to provide users with highly immersive and interactive experiences.
In traditional meetings, someone typically organizes and records the meeting to clarify content afterward. While video conferences now have tools like transcripts to record speakers' words, VR/AR meetings lack tools to help with the recording and assist users. To address this challenge, we develop ARM-RSPA in the research work, which is a real-time assistant system that records meeting content and virtual environment states, summarizes based on user requests, and replays key interactions. Through AR replay, ARM-RSPA provides users with a more convenient and easily understandable way to realize the content of the meetings.
To validate our research, we have conducted various experiments, where ARM-RSPA demonstrates its application in meetings and successfully helps users understand the content explained by speakers. We also discuss the differences between ARM-RSPA and other remote meeting solutions to highlight the high promise of our proposal system. Finally, we also mention our potential developments for other AR meeting tools in the future.
Keywords: VR/AR, Live Stream Summarization, LLM Assistant
基於急診室之心電圖影像與呼吸影片預測住院風險的
深度學習模型
Cardio-Respiratory Deep Learning Model for Predicting Hospital Admission from Emergency Department Electrocardiogram Images and Respiration Videos

急診室擁擠已成為現代醫療體系中的一項重大挑戰,不僅延誤病患的及時治療,也影響資源的最佳分配。臨床醫常依賴快速且主觀的「臨床直覺」評估來輔助分診與決定是否住院。我們假設深度學習模型同樣能利用病患的影像外觀,以更客觀且一致的方式預測住院需求。本研究提出一種創新的心肺雙模態深度學習模型,整合兩種非侵入式資料:從短程呼吸影片中擷取的呼吸波形影像,以及自心電圖(ECG)影像。為了強化模型對關鍵特徵的聚焦,我們引入注意力機制,並使用 Class-Balanced Loss 處理訓練資料中嚴重的類別不平衡。考量只有部分病患提供完整的 ECG 資料,我們先在外部資料集上以 ConvNeXt 架構預訓練 ECG特徵擷取器,以提升心電訊號的表示能力。對於呼吸模態,我們首先在無固定攝影機角度的複雜環境中,自動定位病患的胸部感興趣區域;接著透過 3D 卷積神經網路與雙向長短期記憶(BiLSTM)網路組合,估計呼吸訊號並將其轉換為影像格式,由端到端訓練的 ConvNeXt 模型進行特徵抽取。最後,我們將兩種模態的特徵向量與一個標示 ECG 資料可用性的二元指標串聯,並透過全連接層預測住院結果。
在臺大醫院(NTUH)資料集上的實驗結果顯示,融合 ECG 與呼吸模態的模型達到 AUROC 0.863 和準確率 0.814;僅使用呼吸影片的模型也獲得 AUROC 0.810 和準確率 0.788。這些成果證明本方法具備作為急診室客觀、非侵入式臨床決策支援工具的可行性。
Background: Predicting hospital admission at the emergency department (ED) triage can enable earlier interventions and more efficient resource allocation. Previous approaches, however, have primarily relied on structured data for admission prediction. The use of multimodal data with cardiac and respiratory signals may capture subtle clinical signs to improve the prediction of hospital admission at ED triage.This study aims to develop a reliable and accurate deep learning fusion model that integrates ECG images and respiration video to predict hospital admission at ED triage.We prospectively collected adult ED patient data from National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH), including electrocardiogram (ECG) images and respiration video recorded during triage. The proposed model employs separate modality-specific branches with transfer learning for the ECG branch, explicit modality indicators to handle missing ECG inputs, and a spatial attention module to enhance cardiopulmonary feature extraction. Class-balanced loss was applied to mitigate the impact of dataset imbalance. Model performance was compared against a baseline Taiwan Triage Acuity Score (TTAS) model and single-modality variants. We further evaluated attention heatmaps generated by score-class activation mapping (score-CAM) for interpretability.The dataset comprised 118 patients (positive admission rate: 27%). The proposed ECG–respiration fusion model achieved an accuracy of 0.814, a recall of 0.749, a precision of 0.635, an F1-score of 0.680, an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.863, and an area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.675, outperforming the TTAS baseline and single-modality models. Ablation studies confirmed the contributions of spatial attention and class-balanced loss. Score-CAM visualizations revealed that the model consistently focused on physiologically relevant regions, such as respiratory waveform inflection points.The proposed multimodal deep learning-based model demonstrates strong potential for early hospital admission prediction in the ED, even under incomplete multimodal input conditions. Its integration of ECG and respiration video enhances both the predictive accuracy and interpretability of the existing triage system, making it suitable for addition to real-world triage workflows.
Keywords: Admission, Electrocardiography, Respiration, Deep Learning, Computer Vision
